CROSS-COUPLING REACTIONS OF ALKENYL ACETATES WITH RHODIUM CATALYST
Suzuki-Miyaura coupling is a powerful method for connecting two intermolecular sp2 carbon atoms. Commonly, halogen or sulfonate substituent is used as the leaving group in the electrophilic substrate. However, the electrophilic compounds have a serious impact on the environment. From the viewpoint of the problem, acetate is an ideal leaving group in the cross-coupling reaction.
We found that vinyl acetate worked as an electrophilic substrate in Suzuki-Miyaura coupling by using [RhCl(cod)]2–DPPB catalyst.1) A broad range of substituted styrenes were obtained from vinyl acetate and arylboronic acids through the rhodium catalysis.
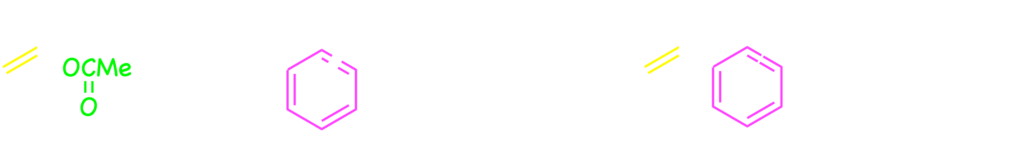
Interestingly, the arylboronic acids were coupled with alkenyl substrates at the β-position of acetate leaving group when the rhodium–cyclooctadiene complex as the catalyst without the bisphosphine ligand.2)
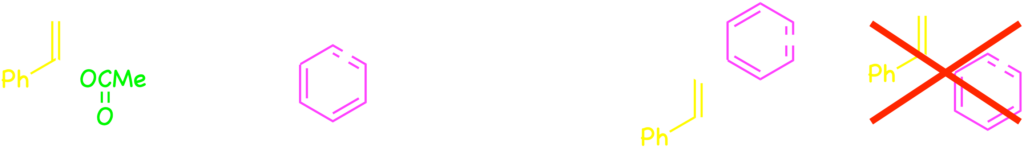
CATALYTIC DEHYDROGENATIVE β-FUNCTIONALIZATION OF ETHYL KETONES3)
Palladium complexes are known to work as the catalyst for the dehydrogenation from alkyl ketones through their enolate intermediates. We combined the palladium-catalyzed dehydrogenation with the nucleophilic 1,4-addition to enones. As a result of the combination, we successfully achieved bond foramation between the nucleophile and the β-carbon of ethyl ketones.3)
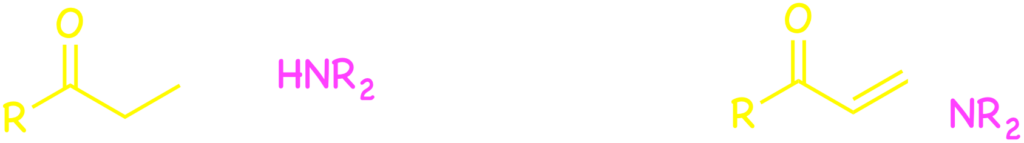
In reactions using an alkyl ketone as a substrate, nucleophiles generally reacts with the carbonyl carbon atom. The α-carbon of the ketone can be functionalized with an electrophile through the enolate intermediate. However, the direct bond formation at the β-position used to be a hard task in synthetic organic chemistry before 2009. Our group realized the β-functionalization by means of the nickel or palladium catalysis with the above approach.
1) Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 48 (39), 7217–7220 (2009). [link to journal article]
2) Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 49 (36), 6396–6399 (2010). [link to journal article]
3) Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 48 (25), 4543–4545 (2009). [link to journal article]
